KALOS
The KALOS process was developed at KIT for the melt-based production of Advanced Ceramic Breeder (ACB) pebbles that will be used as tritium breeders for fusion energy. Not only has the process technology demonstrated its reliability and scalability, but it also offers a simple method for reprocessing the ceramics after use in the reactor.
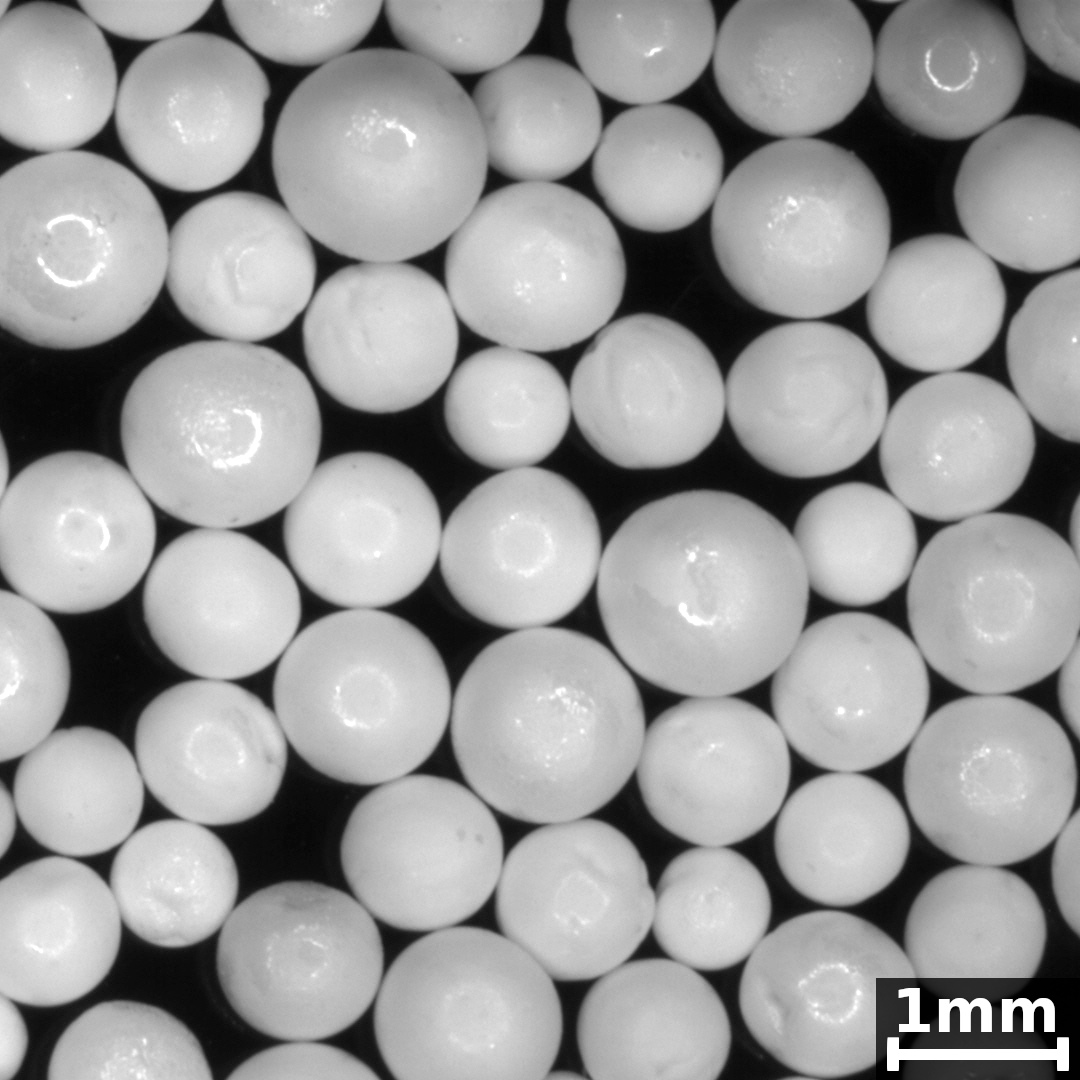
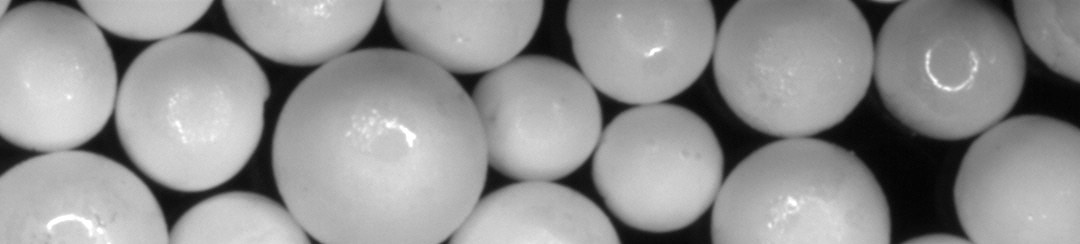
The process is used to produce ACB pebbles consisting of Li4SiO4 and Li2TiO3 for the qualification of breeder blanket designs.
KALOS “Fuelling the Fusion Reaction”
Technical description
Process powders are heated up in a crucible to ~1400 °C to form a melt. Pressure is then applied to the crucible to form a laminar jet through a small nozzle. Selected frequencies are used to control the break-up of the jet, thereby forming individual droplets, which are then solidified using liquid nitrogen in a cooling tower. Recently, the process has been converted from a batch process to a continuous operation with a production rate of 2 kg/h.
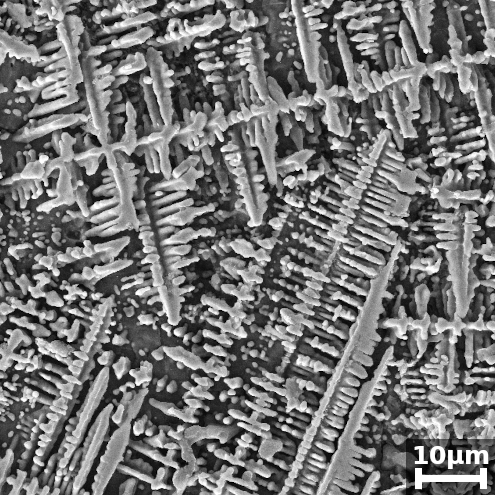
After production, an extensive standardised quality control is performed that includes an analysis of the pebble sizes and distribution, the chemical and phase composition, the open and closed porosities, the mechanical strength of the pebbles, as well as an analysis of the surface morphology and microstructure. Advanced testing of the ACB pebbles includes the long-term thermal stability and the effects of neutron irradiation on the tritium release behaviour and the material properties.
Representative Projects
The KALOS process and ACB development are integral to the qualification of the breeder blanket at KIT:
- KALOS is the only facility currently capable of producing tritium breeding ceramics at a semi-industrial scale within the EU, which is one of the reasons why ACB pebbles are being used for studies in multiple international projects
- ACB pebbles are the solid EU-reference material for tritium breeding and will be featured in future fusion reactor designs such as HCPB and WLCB in DEMO
- The HCCP breeder blanket design, being developed in collaboration with South Korea for testing in ITER, will use ACB pebbles as the tritium breeding material
- The irradiation campaign ACB-TREND (ACB’s in situ Tritium Release Experiment under Neutron irraDiation) is ongoing to test the in-situ tritium release behaviour and tritium residence time of ACB pebbles (WWR-K reactor at INP, Kazakhstan)
- Neutron irradiations in the BR2 reactor at SCK-CEN, Belgium, within the campaign NICE-ACB (Neutron Induced Changes and Effects in ACBs) are underway to investigate the influence on the material properties with post-irradiation examinations taking place at the FML at KIT
Representative publications
- Zhang et al., A high-speed camera-based measurement system for monitoring and controlling the induced jet break-up fabrication of advanced ceramic breeder pebbles, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 136 (2025) 1253–1265; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-14887-9
- Leys et al., Long-term thermal stability of biphasic Li4SiO4–Li2TiO3 EU reference tritium breeder ceramics enriched in Li-6, Nucl. Mater. Energy 43 (2025) 101932; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nme.2025.101932
- Shaimerdenov et al., Rig design development for in situ tritium release studies of EU reference ceramic breeders (ACB-TREND), Fusion Eng. Design 212 (2025) 114851; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2025.114851
- Leys et al., Current status and future perspectives of EU ceramic breeder development, Fusion Eng. Design 164 (2021) 112171; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2020.112171
- Heuser et al., Radiation stability of long-term annealed bi-phasic advanced ceramic breeder pebbles, Fusion Eng. Design 138 (2019) 395–399; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.12.034
- Leys et al., Ceramic pebble production from the break-up of a molten laminar jet, Proceedings of ILASS-Europe 2019, Paris
- Leys et al., The reprocessing of advanced mixed lithium orthosilicate/metatitanate tritium breeder pebbles, Fusion Eng. Design 107 (2016) 70–74; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2016.04.025
Galerie